Geoid
Geoid model
The local terrestrial gravity anomaly model was combined with the global geopotential model by applying the Least Squares Modification of Stokes' formula with Additive Corrections (LSMSA) method to yield the accurate gravimetric geoid modelling results.
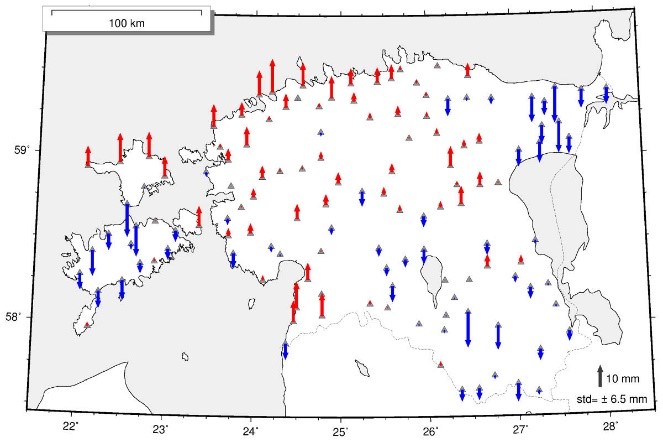
The differences between height anomaly (as approximate of geoid undulation) values with uncertainty of about 5 mm at 131 GNSS-levelling points and LSMSA gravimetric geoid revealed a constant bias of 56.14 ± 0.65 cm. The residuals, after the removal of bias, indicate systematic patterns (Fig. 1) which were modeled by using the least squares collocation prediction method.
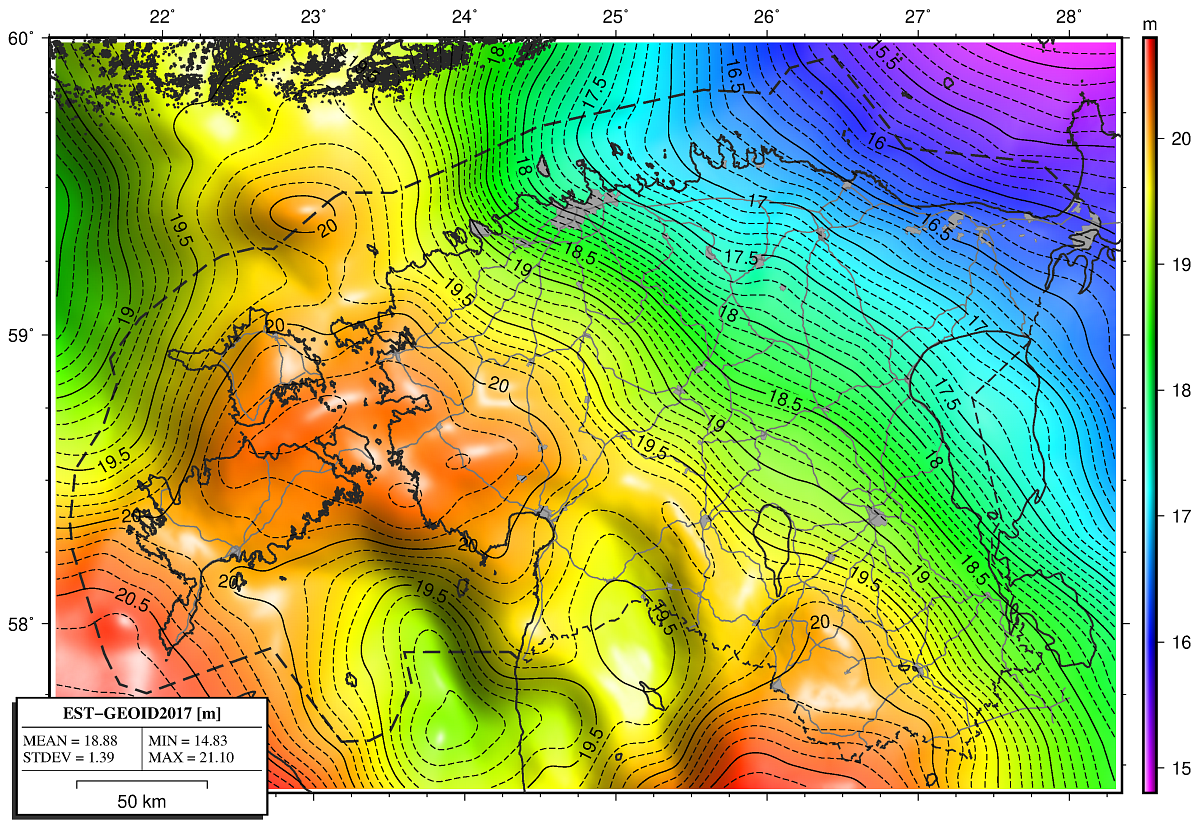
EST-GEOID2017
By combining the gravimetric geoid, the bias and residual surface model, the Estonian national geoid model EST-GEOID2017 was computed with one sigma standard uncertainty of about 5 mm (Fig. 2).
Geoid model EST-GEOID2017 is distributed free of charge, but a licence agreement must be signed. By signing the licensee accepts unilaterally all licensing terms and conditions. The license agreement will be registered in the document management system within 5 (five) working days. After registration, the licensor will notify the licensee by e-mail of the agreement registration number and effective date, and provide all required data in ASCII format within 5 (five) working days.